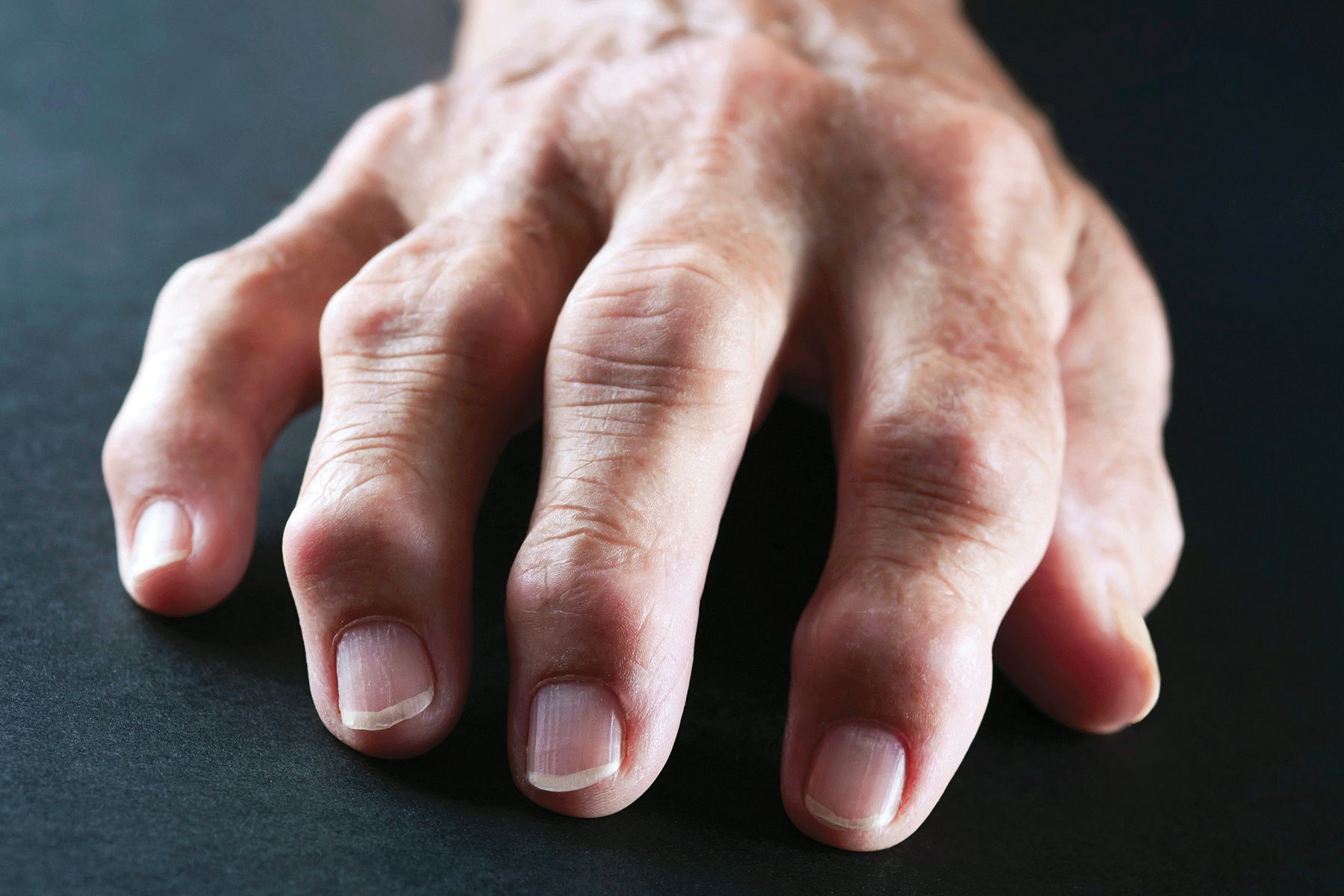
Rheumatoid arthritis causes excruciating symptoms that may limit your mobility, preventing you from enjoying your life. Additionally, it can lead to other diseases such as osteoarthritis and cause damage to other parts of your body. The specialists at the Osteoporosis and Rheumatology Center of Tampa Bay offer effective treatments to prevent the progression of rheumatoid arthritis.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis refers to a progressive autoimmune disorder that causes swelling, pain, and inflammation in your joints. As this disorder progresses, it can result in joint deformity, loss of function, and irreversible destruction. Rheumatoid arthritis can destroy your joints, lungs, skin, blood vessels, and eyes. This disorder occurs when the immune system turns against your body tissues mistakenly. Rheumatoid arthritis destroys your joint linings, leading to common deformity or bone erosion. The inflammation resulting from rheumatoid arthritis can cause detrimental effects on other parts of your body. Early detection of this disorder prevents permanent deformities, and with proper treatment, you can slow down its progression.
How can you know if you have rheumatoid arthritis?
The signature symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are inflammation and chronic joint pain. RA leads to irreversible destruction of the same type of joint on both limbs. This is how you can distinguish this form of arthritis from other conditions such as osteoarthritis. Your signs and symptoms exacerbate as the disease worsens. Your symptoms may include:
- Joint deformities and loss of joint function
- Loss of appetite
- Excruciating pain in the affected joints
- Unexplained fatigue
- Weakness
- Low-grade fever
- Swollen, warm, and tender joints
- Joint stiffness that worsens after a long period of inactivity or in the morning
Early rheumatoid arthritis affects smaller joints such as your fingers and your toes. As the disease deteriorates, it may spread to your knees, elbows, wrists, shoulders, hips, and ankles. Periods of severe symptoms are medically known as flares, alternating with periods of remission. Over time, your joints may shift out, limiting your walking ability.
What factors increase your risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis?
The causative factors of rheumatoid arthritis are unknown, but factors may increase your chances of developing it. They include:
- Your sex. Women are more vulnerable to getting rheumatoid arthritis
- Being overweight
- Family history of the disease
- Smoking
- Age. Older adults are more likely to develop the disorder
How can you treat arthritis?
Medical experts are yet to discover a cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but several noninvasive and invasive procedures can slow its progression. Your doctor may begin by recommending antirheumatic drugs to prevent complications resulting from the disease. Your treatment depends on the severity of your health condition. Your doctor may recommend may also recommend the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate your pain
- Corticosteroid medications like prednisone to prevent joint damage
- Conventional DMARDS
- Biologic response modifiers
- Therapy
- Surgery
You can also adopt healthy lifestyle habits to supplement your medications. You try exercising regularly, relaxing, and applying cold or heat to reduce the intensity of your symptoms.
For more information about rheumatoid arthritis, call the Osteoporosis Rheumatology Center office or book your spot online.